NARROW DIAMETER IMPLANT IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE
Case information
Physical exam: 46 missing, the alveolar was blade-shaped, the mucosal color was normal, and the width of the keratinized gingiva on the cheek and lingual crest was about 2mm. The gap in the missing area is normal, 47 is mesial-inclined, loose (-), the antagonist is normal, and the occlusal gap is normal.
Auxiliary exam: CBCT showed no sever alveolar bone resorption in the 46 missing area, and the top of the alveolar ridge is 19.89 mm away from the inferior alveolar nerve tube, with the medium bone. The adjacent teeth had no periapical lesions, and the alveolar bone had no abnormal lesions.
Diagnosis: dentition defect
Treatment plan: 46 implant restoration
Case source : Shenzhen University General Hospital

Workflow
1. Preoperative CT
-

Panoramic X-ray -

Implant area
2. Intraoral Scan
Acquire data with SHINING 3D’s Aoralscan intraoral scanner




3. Surgical Plan
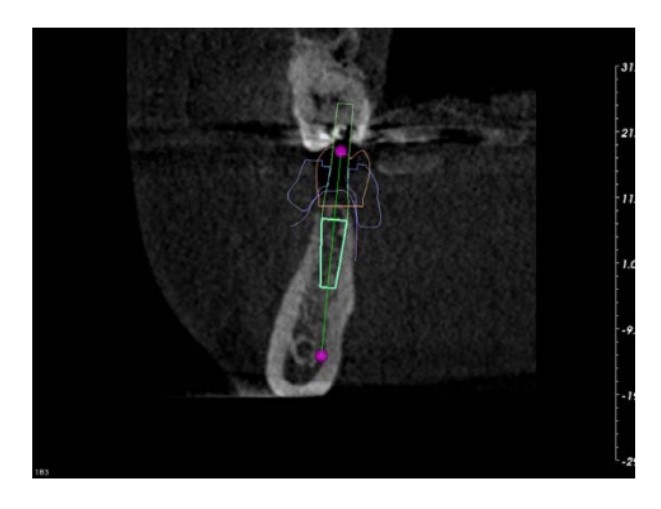
Tooth position: #46
Diameter of implant: 3.70mm
Extend length of drill: 8.50mm
Length of implant: 11.50mm
Drill depth: 20.00mm
Diameter of implant tip: 2.50mm
Extend length of drill: 8.50mm
Gingiva incision: 3.70mm
Pin/handle: D2.0/L20.00

4. Print model & guide with AccuFab-C1
-

Printed model -

Printed guide -

Try-in on the printed model
5. Surgical procedure
Preoperative photo


Position the surgical guide, then incise gingiva and drill pilot hole. Check depth and condition of pilot hole.


Profile drill for implant. Insert the implant.


Seat the implant. Fix the implant by torque wrench.


Place the healing cap.

Postoperative photo

6. Postoperative CT

Summary
Severe bone resorption at the buccal and lingual, along with narrow mesiodistal space is unfavorable for manual implantation. The use of surgical guide ensure the position and depth of drill hole, benefiting the accuracy and safety of this surgery.


















Leave a comment